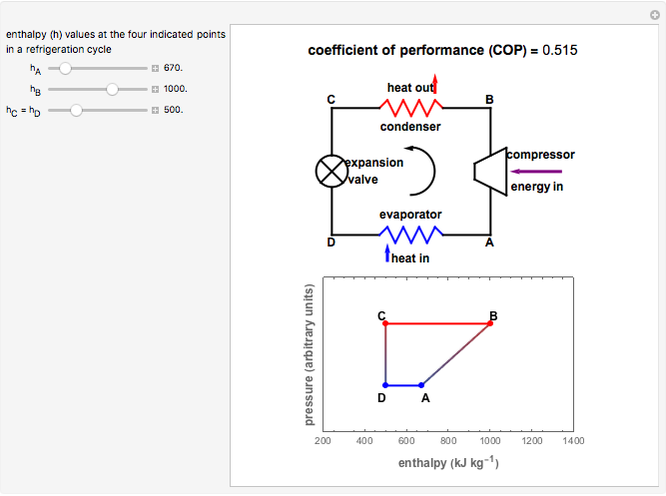
The coefficient of performance COP of a refrigerator is defined as the heat removed from the cold reservoir Q cold ie inside a refrigerator divided by the work W done to remove the heat ie the work done by the compressor. The coefficient of performance of a heat pump is greater than unity so the work required is less than the heat transferred making a heat pump a more efficient form of heating than electrical resistance heating.
Refrigeration Cycle Coefficient Of Performance Wolfram Demonstrations Project
The purpose of a refrigerator is the removal of heat called the cooling load from a low-temperature medium.

. For temperature difference of about 25C 45 20 the COP may. As can be seen the better more efficient the refrigerator is when more. The performance of the PVT solar system is evaluated at several levels of solar irradiation of 500 600 700 800 900 and 960 wm 2.
As can be seen the better more efficient the refrigerator is when more. The lower the kWton - the more efficient the system. The warming is due to changes in the internal state of the material releasing heat.
The term is defined as the ratio of energy consumption in kW to the rate of heat removal in tons at the rated condition. The schematic sketch of double-effect system is shown in Fig. The coefficient of performance COP of a refrigerator is defined as the heat removed from the cold reservoir Q cold ie.
B and h are the regression coefficients different for every regression. 1 kW of power input is required. Download Refrigeration Lab Report2037 PDF for free.
P w electrical input energy W If a heat pump delivers 3 units of heat for every unit of energy input - the COP is 3. A heat pump has a COP value 5 means. Regression equation for heating no cooling with no day normalization E b hHDD Where.
Vapours of refrigerants are generated. For air v Relative speed of the object through the air. As well as asses its performance by measuring the isentropic efficiency which was 599 and the COPR coefficient of performance 1949.
Coefficient of Performance Refrigerator Air Conditioner. Natural Convection 5 25 Wm² K. Example - COP Heat Pump Cooling Cycle.
Formula for Convective heat transfer coefficient Calculation. 1 kW of power input is required to extract 4 kW of heat from the evaporator. Where h is the enthalpy in the system.
The work done by the compressor. The coefficient of performance COP of a refrigerator is defined as the heat removed from the cold reservoir Q cold ie. The temperature of the plate the water intake and the outflow have all been measured using a set of thermocouples placed in the proper positions.
The temperature of the mean PV cells and the glass has been measured using a set. A magnetocaloric material warms up when a magnetic field is applied. Inside a refrigerator divided by the work W done to remove the heat ie.
Refrigeration Cycles The vapor compression refrigeration cycle is a common method for transferring heat from a low temperature to a high temperature. HDD is the heating degree days over the period in question a month in the example above. KWton P c Q r 1 where.
Convective Heat Transfer coefficient for Air. COP Coefficient of Performance. Refrigeration is the process of transferring energy from a low energy domain to a high energy.
P c electrical power consumption kW Q r heat. Some of the Vapor Compression Refrigeration Cycle Problems that may affect this value are. Coefficient of Performance Refrigerator Air Conditioner.
Magnetic refrigeration is a cooling technology based on the magnetocaloric effectThis technique can be used to attain extremely low temperatures as well as the ranges used in common refrigerators. A simple and practical absorption system using ammonia as refrigerant and water as absorbent described in the previous articles is an example of single-effect cycle system for vapour absorption refrigeration system. The above figure shows the objectives of refrigerators and heat pumps.
Inside a refrigerator divided by the work W done to remove the heat ie. It is basically the amount of refrigerating effect per unit power input. Forced Convection 10 200 Wm² K.
This formula works for a. 1 kW 1000 W 3413 Btuh. H h heat produced Btuh J kWh h w equivalent electric energy input Btuh J kWh 3413 P w.
Knowing that the aim of the refrigerator is heat removal and that this process requires work the COP of the cycle becomes. Also be aware of the fact that temperature dependency can be significant for example a 5-10 increase for metals over a temperature rise of 30C. An air conditioner has a COP value 5 means.
E is the energy usage over the period in question a month in the example above. A heat pump. B is the intercept or constant 31993 in.
The work done by the compressor. The purpose of a heat pump. 1 kW of power input is required to extract 5 kW of heat from the evaporator.
A refrigerator has a COP value 4 means. The term kWton is commonly used for larger commercial and industrial air-conditioning heat pump and refrigeration systems. As the temperature of the higher-temperature reservoir increases in response to the heat flowing into it the coefficient of performance decreases causing an increasing.
The Coefficient of Performance COP expresses the efficiency of this cycle. It is pretty confusing that the Seebeck coefficient may be defined as an absolute value or relative to a reference material as is the case for Table 1 where the reference material is platinum. The COP strongly depends on outside temperature and required indoor temperature.

Thermodynamics Real Refrigeration Cycle Carnot Refrigeration Cycle Youtube

Vapour Compression Refrigeration Cycle L Thermodynamics L Gate 2020 Mechanical Youtube

How Does The Cop Of Refrigerator Is Greater Than 1 Quora

Example Computing Refrigeration Coefficient Of Performance Youtube
0 Comments